Hugo's Blog
LeetCode 1382. Balance a Binary Search Tree - Easy Solution | Go
Link 👉🏻 1382. Balance a Binary Search Tree

Description
Given the root of a binary search tree, return a balanced binary search tree with the same node values. If there is more than one answer, return any of them.
A binary search tree is balanced if the depth of the two subtrees of every node never differs by more than 1.
Example 1:
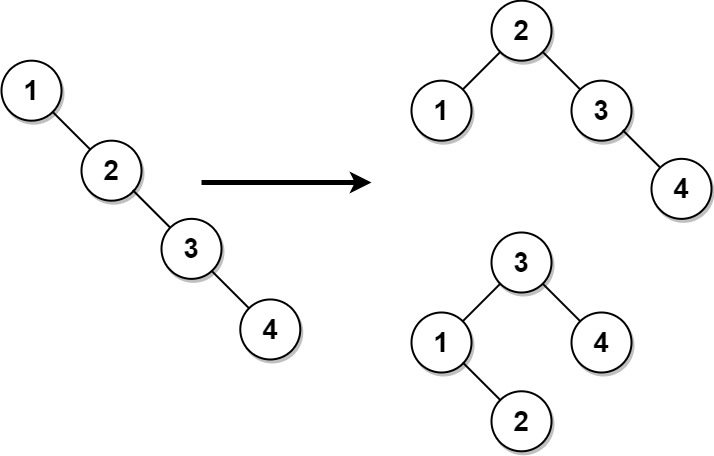
- Input:
root = [1,null,2,null,3,null,4,null,null] - Output:
[2,1,3,null,null,null,4] Explanation: This is not the only correct answer, [3,1,4,null,2] is also correct.
Example 2:
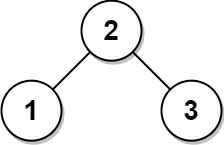
- Input:
root = [2,1,3] - Output:
[2,1,3]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 104]. 1 <= Node.val <= 105
Intuition
With Depth-First Search (DFS), we can traverse a tree and store its nodes in an array. Once we have this array, we can construct a new tree using in-order traversal. This is done by dividing the array in half and recursively building the left and right subtrees from the respective halves.
{% notel blue Note %}
How to implement slicing in Go? Golang slice append 實作細節
var nums []int nums = append(nums, 1) // append 1 to the slice
{% endnotel %}
Approach
- Traverse the tree using Depth-First Search (DFS) and store the nodes in an array.
- Construct a new tree using the array from step 1.
- Recursively build the left and right subtrees from the respective halves of the array.
- Return the root of the new tree.
Complexity
- Time complexity: $O(N)$
- Space complexity: $O(N)$
Code
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * type TreeNode struct { * Val int * Left *TreeNode * Right *TreeNode * } */ func balanceBST(root *TreeNode) *TreeNode { var arr []*TreeNode var dfs func(*TreeNode) dfs = func(n *TreeNode) { if n.Left != nil { dfs(n.Left) } arr = append(arr, n) if n.Right != nil { dfs(n.Right) } } dfs(root) var build func(int, int) *TreeNode build = func(l, r int) *TreeNode { if l >= r { return nil } mid := (l + r) / 2 n := arr[mid] // root n.Left = build(l, mid) n.Right = build(mid+1, r) return n } return build(0, len(arr)) }